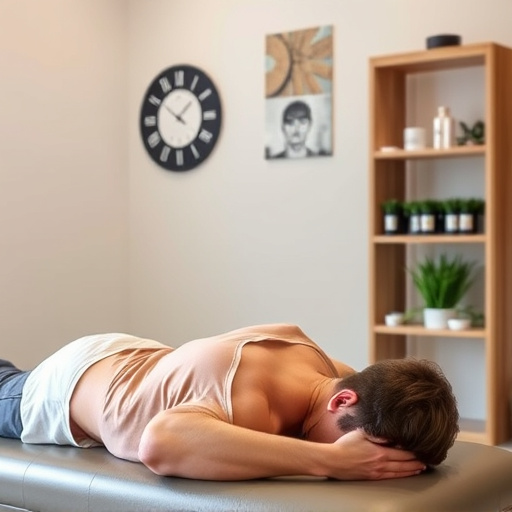
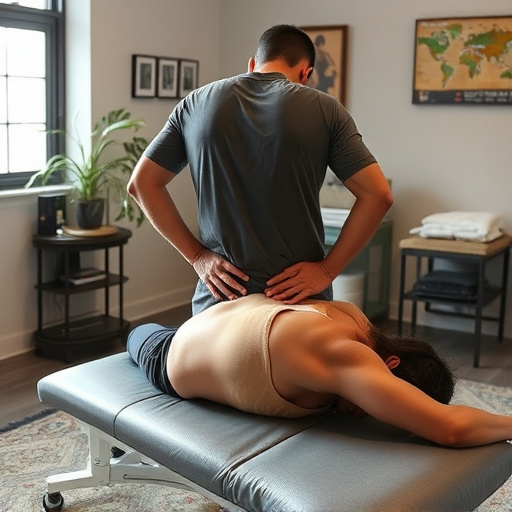
Ergonomic injuries in the digital age stem from prolonged sitting, repetitive tasks, and harsh working conditions. Causes include incorrect posture, poor setup, heavy lifting, and localized tension. Risk factors are job-related (repetition, force, awkwardness) or individual (poor fitness, lack of knowledge, prior injuries). Early diagnosis through patient history, exams, and tests is key for personalized treatment focusing on headache and nerve relief. This involves rest, therapy, exercises, workplace modifications, physical therapy, manual therapy, occupational therapy, heat/cold therapy, relaxation techniques, and structured guidance to prevent chronic pain and future injuries.
Ergonomic injury treatment is essential for addressing repetitive stress conditions, a growing concern in today’s digital age. Many professionals face risks of injury from prolonged exposure to poorly designed workstations and repetitive tasks. This article delves into understanding these injuries, their causes, and risk factors. We explore effective diagnosis methods and comprehensive treatment strategies for a full recovery. By implementing ergonomic principles, individuals can prevent and manage these conditions, enhancing overall well-being at work and beyond.
- Understanding Ergonomic Injuries: Causes and Risk Factors
- Diagnosing Repetitive Stress Conditions Effectively
- Comprehensive Treatment Strategies for Recovery
Understanding Ergonomic Injuries: Causes and Risk Factors

Ergonomic injuries are a growing concern in today’s digital age where many individuals spend extended periods sitting at desks or staring at screens. These injuries result from repetitive tasks and prolonged exposure to strenuous working conditions, often leading to discomfort and pain. Understanding the causes and risk factors is the first step towards effective ergonomic injury treatment.
Common causes include incorrect posture, inadequate workstation setup, heavy lifting, and prolonged periods of tension or strain on specific body parts, such as the hands, wrists, elbows, shoulders, back, and neck. Risk factors can be categorized into job-related and individual factors. Job-related risks may include repetitive tasks, excessive force required to perform duties, and awkward working positions. Individual risk factors encompass poor physical condition, inadequate knowledge of ergonomic principles, previous injuries, and certain medical conditions like arthritis or carpal tunnel syndrome. Identifying these causes and risk factors is crucial in designing personalized treatment plans, including headache relief strategies and pinched nerve relief measures, to prevent further damage and promote recovery.
Diagnosing Repetitive Stress Conditions Effectively

Diagnosing repetitive stress conditions (RSCs) effectively is a crucial step in ergonomic injury treatment. Healthcare professionals utilize a combination of patient history, physical examinations, and specialized tests to pinpoint the root cause of symptoms. This involves assessing work or activity patterns that may contribute to the development of RSCs, such as prolonged typing, frequent lifting, or repetitive movements. During the examination, doctors look for signs of tenderness, swelling, or reduced range of motion in affected areas. Specialized diagnostic tools, like electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies, may be employed to evaluate nerve function and identify any damage or compression.
Early identification is key to managing chronic pain associated with RSCs. Once diagnosed, a comprehensive approach to ergonomic injury treatment can begin. This typically includes rest, ice or heat therapy, over-the-counter pain relievers, and therapeutic exercises tailored to target specific muscle groups affected by the condition. Additionally, occupational therapists play a vital role in modifying work environments to promote better posture, reduce strain, and prevent future injuries, thereby aiding in chronic pain management and muscle recovery.
Comprehensive Treatment Strategies for Recovery

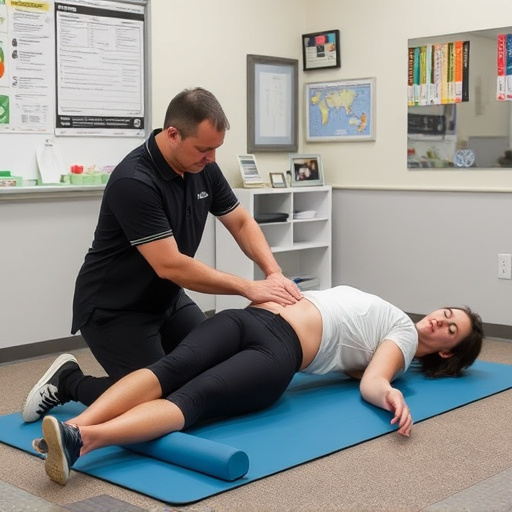
Ergonomic injury treatment for repetitive stress conditions requires a comprehensive approach to ensure complete recovery. This often involves a combination of various strategies tailored to address the specific needs of each individual. Physical therapy is a key component, focusing on exercises that strengthen and stretch relevant muscles to improve posture and reduce strain. Additionally, modifying work environments and implementing ergonomic principles can prevent future injuries by promoting better postural alignment and reducing excessive forces on joints and tissues.
Rehab services play a crucial role in providing structured guidance and support during the recovery process. This may include specialized treatments like manual therapy, massage, or occupational therapy to enhance healing and restore functionality. Furthermore, managing pain through non-pharmacological methods such as heat/cold therapy, electrical stimulation, or relaxation techniques can significantly contribute to headache relief and overall comfort during rehabilitation.
Ergonomic injury treatment for repetitive stress conditions involves a multifaceted approach, from effective diagnosis to comprehensive strategies that promote recovery. By understanding the causes and risk factors associated with these injuries, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent them. Through proper diagnostic methods, those suffering can receive tailored treatments that address the root causes. With the right combination of rest, modifications to work environments, and targeted therapies, many repetitive stress conditions can be successfully managed and prevented from becoming chronic. Prioritizing ergonomic injury treatment is essential for maintaining productivity, comfort, and overall well-being in both professional and personal settings.